Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wu, P.*; Murai, Naoki; Li, T.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Xia, K.*; Peng, K.*; Zhang, Y.*; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 25(1), p.013032_1 - 013032_11, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Hasegawa, Yuta; Aoki, Takayuki*; Kobayashi, Hiromichi*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Onodera, Naoyuki
Parallel Computing, 108, p.102851_1 - 102851_12, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:42.85(Computer Science, Theory & Methods)The aerodynamics simulation code based on the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) using forest-of-octrees-based block-structured local mesh refinement (LMR) was implemented, and its performance was evaluated on GPU-based supercomputers. We found that the conventional Space-Filling-Curve-based (SFC) domain partitioning algorithm results in costly halo communication in our aerodynamics simulations. Our new tree cutting approach improved the locality and the topology of the partitioned sub-domains and reduced the communication cost to one-third or one-fourth of the original SFC approach. In the strong scaling test, the code achieved maximum 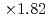 speedup at the performance of 2207 MLUPS (mega- lattice update per second) on 128 GPUs. In the weak scaling test, the code achieved 9620 MLUPS at 128 GPUs with 4.473 billion grid points, while the parallel efficiency was 93.4% from 8 to 128 GPUs.
speedup at the performance of 2207 MLUPS (mega- lattice update per second) on 128 GPUs. In the weak scaling test, the code achieved 9620 MLUPS at 128 GPUs with 4.473 billion grid points, while the parallel efficiency was 93.4% from 8 to 128 GPUs.
Gubler, P.; Sato, Daisuke*
Physical Review D, 96(11), p.114028_1 - 114028_20, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:28.59(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Exact sum rules for the longitudinal and transverse part of the vector channel spectral functions at nonzero momentum are derived in the first part of the paper. The sum rules are formulated for the finite temperature spectral functions, from which the vacuum component has been subtracted, and represent a generalization of previous work in which sum rules were derived only for the zero-momentum limit. In the second part of the paper, we demonstrate how the sum rules can be used as constraints in spectral fits to lattice data at various temperatures, with the latest dynamical lattice quantum chromodynamics data at zero momentum.
Yamauchi, Hiroki; Igawa, Naoki; Ishii, Yoshinobu
Proceedings of 5th International Conference on Gas Hydrates (ICGH-5), Volume 5, p.1615 - 1618, 2005/06
Inelastic neutron scattering experiments were carried out on powdered methane hydrate. In order to observe the precise spectra inelastic neutron scattering without the influence of incoherent contribution, the fully deuterated sample was used for the measurements. The relatively clear excitation peaks were observed at about 6.5 meV and 10 meV mainly corresponding to the transverse acoustic modes and exhibited only very little temperature dependence at 10 K and 100 K. On the other hand, the small shoulder found around 4 meV at 10 K showed apparent temperature dependence. The scattering intensity of this shoulder appeared to broaden and decrease at 100 K, which can be attributed to the increasing anharmonic contribution to the translational motion of the methane molecules encaged in the large cages.
Ebihara, Kenichi
JAERI-Research 2005-004, 121 Pages, 2005/03
This report is the JAERI's report version of the doctor thesis by the author. In this report, first, the validity and usefulness of the application of the two-phase fluid model of the lattice-gas method and the lattice Boltzmann method(LBM) are examined. On the basis of the examination, next, the horizontal stratified two-phase flow that is the fundamental and important flow is simulated by the HCZ model which is one of the two-phase fluid model of the LBM. It is seen that the interfacial growth of the HCZ model satisfies the Kelvin-Helmholtz instability theory and reproduces the theoretical two-phase flow regime map of Taitel and Dukler(T-D map). It is found that more superficial flow velocity of the rare phase is necessary in the channel with the narrow width. The HCZ model can also simulate the droplet generation accompanying more complex interfacial phenomena and reproduce the experimental correlation of Ishii and Grolmes in the range of the distribution of the experimental data.
Ebihara, Kenichi; Watanabe, Tadashi
Proceedings of 2004 ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition (IMECE '04) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2004/11
This paper describes the numerical simulation of the interfacial growth of the stratified wavy two-phase flow in the horizontal rectangular channel. The influence of the channel width upon the growth of the interfacial wave was evaluated by the several simulations for the different channel width. The numerical simulation model adopted in this paper is a one-component two-phase fluid model of the lattice Boltzmann method. The wave growth was observed and the dimensionless numbers that characterize the two-phase flow state were measured during the computations. The relation between the wave growth and the dimensionless numbers, which characterize the flow state, was compared with that in the flow pattern map proposed by Taitel and Dukler. It was verified in the case of the wide channel width that the simulated relation was almost in agreement with that in the flow pattern map. It was shown that the narrower the channel width became, the more mass flow rate of the rare phase the interfacial growth needed and the obtained relation deviated from that in the flow pattern map.
Ebihara, Kenichi
Tsukuba Daigaku Daigakuin Shisutemu Joho Kogaku Kenkyuka Hakase Gakui Rombun, 134 Pages, 2004/09
In this thesis, first the liquid-gas models of the lattice method are examined by applying them to two-phase flow simulations. Next the liquid-gas model(the HCZ model) of the lattice Boltzmann method is applied to the three-dimensional simulation of the horizontal stratified two-phase flow. The following results are obtained. (1)The two- and three- dimensional interface simulated by the HCZ model satisfies the Kelvin-Helmholtz instability theory. (2)In the simulation of the interfacial growth in the rectangular channel, it is found that the relation between the interfacial growth and the flow state is in agreement with the flow regime map proposed theoretically by Taitel and Dukler. (3)It is also found that the three dimensionality becomes remarkable and the interfacial growth needs more flow rate of the rare phase than that of the theoretical flow regime map when the channel width is narrower. (4)In the droplet creation simulation, it is found that the relation between the droplet creation and the flow state simulates the experimental correlation proposed by Ishii and Grolmes.
Ebihara, Kenichi; Watanabe, Tadashi
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu, B, 70(694), p.1393 - 1399, 2004/06
The horizontal stratified two-phase flow in the rectangular pipe whose width in smaller than the height is simulated by the one-component two-phase lattice Boltzmann method. The interfacial growth between two phases is measured for three cases with the different pipe width and the measured dimensionless number charactering the two-phase flow is compared with the flow regime map proposed by Taitel and Dukler. It is found that the boundary separating the interfacical growth from the non-growth which is obtained by the simulations is larger in the flow regime map when the pipe width is narrower.
 with a sublattice formalism; Equilibria involving the nonstoichiometric nitrides
with a sublattice formalism; Equilibria involving the nonstoichiometric nitridesOgawa, Toru
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 201, p.284 - 292, 1993/00
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:76.55(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 52(2), p.549 - 555, 1983/00
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:80.99(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
JAERI-M 5245, 65 Pages, 1973/04
no abstracts in English

 -Ni
-Ni
;
Proc.Symp.on Neutron Inelastic Scattering, p.181 - 186, 1968/05
no abstracts in English